Water Purifier / Water Dispenser

Want to drink more cleaner water at your home? Choose a high quality water purifier that works with the latest technology to filt the water.
Likes the OLANSI water purifiers, make the best direct drinking water for your health.

Hydrogen-rich Water

RO rReverse Osmosis Membrane

Quick Heating / 3 Seconds Will Be Hot

Random Temperature Control

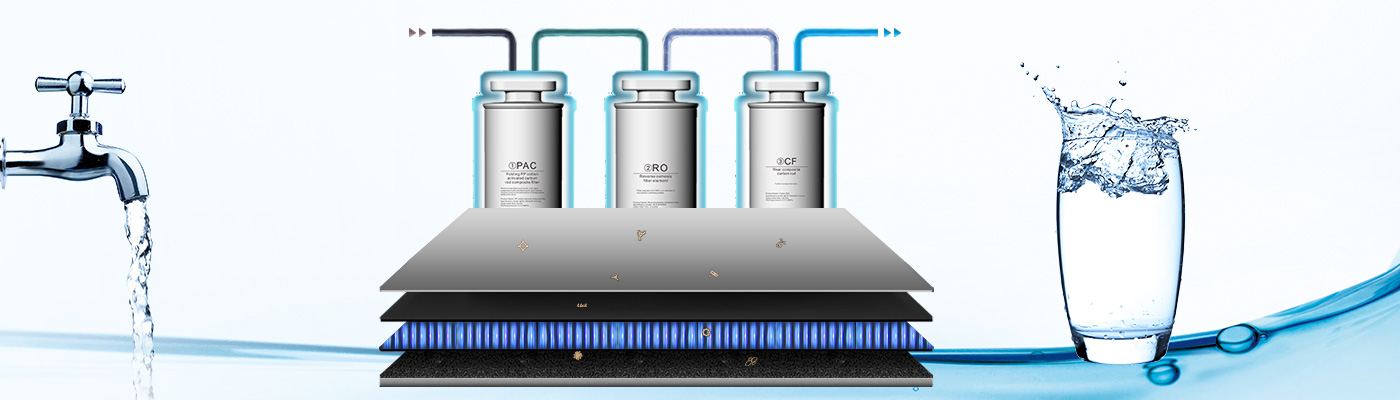
Multiple Filtering
1. Reverse osmosis depth filtration technology
2. Quick heating, 3 seconds is hot
3. Free installation
4. The separation design of strontium-rich carbon bar composite filter core and wastewater box
5. Multiple temperature effluent
6. Remind of filter element replacement monitoring
7. PAC composite filter
8. RO Reverse osmosis membrane
9. Rear carbon rod filter
10. Electrolysis hydrogen water
11. Hydrogen-rich water
12. Random temperature control
13. Multiple Filtering
14. Water Sterilization
15 .Filter color and odor
OLANSI Water Filting Technology Research Fields
Global water treatment product manufacturers are exploring state-of-the-art water filtration technologies such as carbon nanotubes and advanced membrane systems to better serve their customers. OLANS’s water purifier R&D is applied three of the latest water purification technologies that are likely to serve as alternatives to existing water purification processes.
1. Nanotechnology
Nanotechnology involves several approaches and processes of applying materials on the atomic or molecular scale. Nanotech-based water purification processes are considered to be modular, highly efficient and cost-effective when compared to conventional water purification methods.
The nanotechnology-based purification processes are considered to be highly efficient and cost-effective. The major applications of nanotechnology in water treatment processes include silver, copper and zero-valent iron (ZVI) nanoparticles, nanostructured photocatalysts, nano-membranes, and nanoadsorbents.
The large surface-to-volume ratio of nanoparticles enhances the adsorption of chemical and biological particles, while enabling the separation of contaminants at very low concentrations. Nanoadsorbents feature specific physical and chemical properties for the removal of metallic pollutants from water.
Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) are considered to be one of the prominent nanomaterials used in water purification. CNT-based filtration systems can remove organic, inorganic and biological compounds from water.
2. Acoustic nanotube technology
The acoustic nanotube technology employs acoustics in place of pressure to direct water through small-diameter carbon nanotubes.
The technology is based on an acoustically driven molecular screen integrated with carbon nanotubes that allow the passage of water molecules while blocking any larger molecules and contaminants. It consumes less power than traditional filtration systems and drives water away from contaminants instead of removing pollutants from water. The process also eliminates the need for flushing the filter system.
The primary applications of acoustic nanotube technology are municipal water plants, medical facilities, laboratories, distilleries, desalination plants, industrial facilities, wastewater treatment plants, and consumer segment. The innovation is scalable with the integration of multiple filters, according to the filtration needs of users.

3. Photocatalytic water purification technology
Water treatment using photocatalysis has gained prominence in recent years due to its efficiency in treating contaminated water. The technology utilises photocatalyst and ultraviolet (UV) rays to remove toxic substances from water.
Panasonic developed a technology that binds the photocatalyst (titanium dioxide) to a commercial adsorbent and a catalyst called zeolite, ensuring effective separation and recovery of photocatalysts from the water for reuse. Titanium dioxide can mineralise a range of organic compounds into safe end products. The catalyst uses UV radiation either from sunlight or artificial light to separate substances.
Photocatalysis can break down a range of organic materials, estrogens, pesticides, dyes, crude oil, and microbes such as viruses and chlorine-resistant pathogens, as well as inorganic compounds such as nitrous oxides.
Photocatalytic water treatment systems are suitable for use in water and wastewater treatment facilities and can treat industrial wastewater polluted with high loads of organic substances or metals.